When evaluating ERP systems, architecture often determines how well the platform performs, scales, and integrates with existing business systems. The same holds for SAP Business One, whose streamlined yet powerful SAP architecture is a key reason it’s so effective for small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
Unlike legacy systems that rely on rigid, monolithic setups, SAP Business One is designed around a flexible client–server architecture that supports both on-premise and cloud deployments. This structure gives users the reliability of local control and the agility of cloud computing, two critical factors for modern businesses.

Understanding the SAP Business One System Architecture
At its core, the SAP Business One system is built on a two-tier client–server architecture. This framework separates the presentation layer (what users interact with) from the business logic and database layers (where processing and data management happen). The result is a robust and efficient environment that supports real-time transactions, analytics, and integrations.
Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Client Layer | The user interface that allows employees to interact with SAP modules. Typically installed on Windows desktops, though web and mobile clients are also supported. Users can perform transactions, view reports, and access dashboards seamlessly. |
| Server Layer | Handles core processing, database transactions, and business logic. It can run on Microsoft SQL Server or on SAP HANA, depending on performance requirements and chosen deployment. |
| Database Layer | Stores and manages all master and transactional data. When deployed on SAP HANA, it uses in-memory computing for instant access and analytics. |
This design ensures that most computational load and data processing occur on the server side, allowing client machines to remain lightweight and responsive.
SAP Business One on SQL vs SAP HANA
One of the strengths of SAP Business One lies in its architectural flexibility. It can run on either Microsoft SQL Server or SAP HANA.
- SQL Server Deployment: A traditional setup that offers stability and cost efficiency. It’s suitable for SMEs with moderate reporting needs and simpler infrastructure.
- SAP HANA Deployment: Built for performance-driven businesses, HANA’s in-memory technology enables real-time analytics, predictive insights, and lightning-fast query responses. It also supports advanced data visualization and forecasting through the SAP Analytics module.
In both configurations, the SAP architecture maintains the same logical structure, with differences primarily in database speed and analytical capability.
Cloud and On-Premise Flexibility
SAP Business One can be deployed on-premise, in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment.
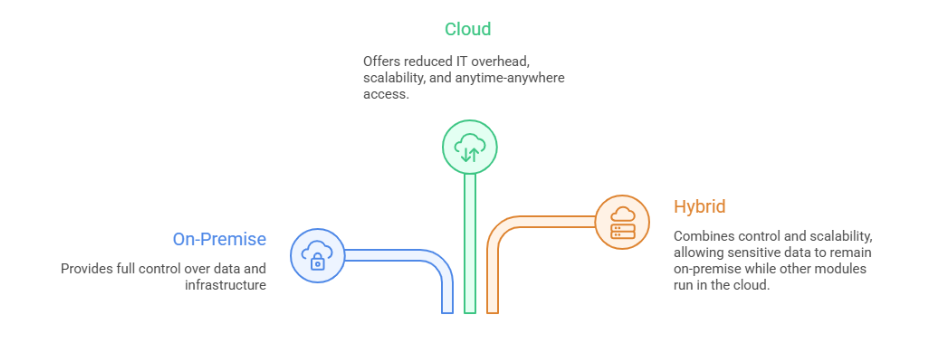
This adaptability is what makes the SAP Business One system particularly attractive to SMEs with evolving IT strategies.
How the Architecture Enables Business Performance
The structure of SAP Business One directly influences what the platform can do and how effectively it does it. Here’s how its architecture enhances business outcomes:
- Real-Time Processing: The client–server model, combined with SAP HANA’s in-memory database, ensures near-instant data access and analysis.
- Seamless Integration: APIs and integration frameworks connect SAP Business One with CRMs, e-commerce platforms, and third-party applications without disrupting data consistency.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, the system’s modular architecture enables the easy addition of new functions, users, and locations.
- Security and Stability: Centralized data management and role-based access controls maintain security and ensure data integrity across departments.
- Lower Maintenance: In the cloud, system upgrades and patches are handled seamlessly, reducing IT dependency and downtime.
How to Use SAP Business One Effectively
Knowing the underlying SAP architecture helps businesses understand how to use SAP Business One strategically.
By understanding how data flows between the client and server layers, businesses can configure the system more effectively, troubleshoot more quickly, and integrate more seamlessly with other tools.
In practical terms, here’s what SAP Business One can do when implemented well:
- Automate routine operations and eliminate manual duplication.
- Improve inventory accuracy and financial reporting.
- Deliver live dashboards for smarter, data-driven decisions.
Best practices include:
- Defining user roles carefully to optimize access control.
- Scheduling routine database maintenance and health checks.
- Leveraging HANA dashboards for real-time analytics and reporting.
- Partnering with a certified SAP expert for upgrades and optimization.
These measures ensure that your SAP Business One system continues to deliver efficiency and insight as your organization scales.
Conclusion
The SAP Business One architecture is intentionally designed for flexibility, scalability, and performance, making it a perfect fit for growing SMEs. Its client–server structure, paired with SQL or HANA deployment options, delivers real-time insights and secure, centralized control across all operations.
Ultimately, knowing how the system works helps you maximize what SAP Business One can do for your organization.
If you’re looking to implement or optimize your SAP Business One system, Praxis Info Solutions can help. As an authorized SAP partner with over 13 years of ERP experience, Praxis delivers tailored solutions across more than 15 industry verticals. With 120+ successful implementations worldwide, our team ensures smooth deployments, seamless integrations, and ongoing support so your business runs smarter every day.
Book a demo with Praxis Info Solutions today to explore how SAP Business One can be architected for your business success.


